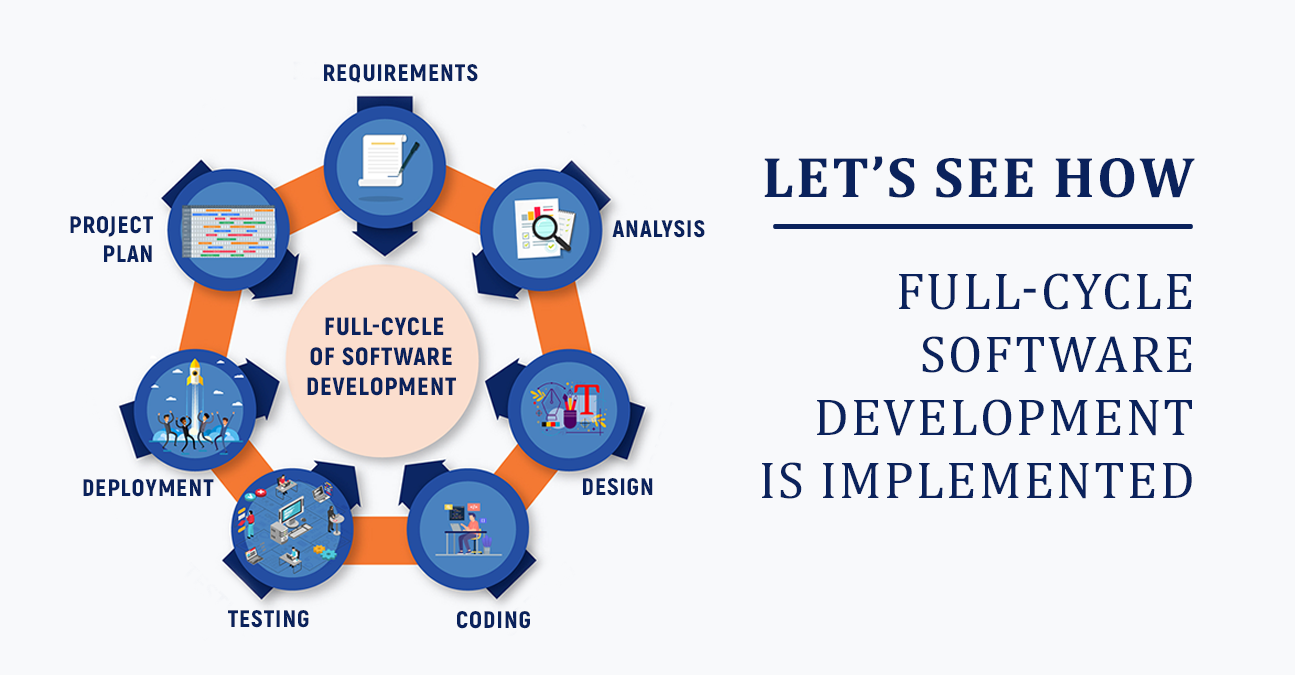
Full-cycle software development can be defined as the entire lifecycle of any software product, in which it’s planned, designed, developed, tested, and delivered to the end user. This type of methodology is used by all kinds of companies today.
Let’s see how full-cycle software development is implemented and the various terms associated with FCSD.
1. Static Code Analysis
Static Code Analysis (SCA) is a process in which computer software source code is analyzed without actually executing it. This typically involves examining the text of source code, looking for various types of errors, and reporting them to developers who can then make corrections. Static analysis tools are often used by programmers during development to improve software quality, find bugs or potential problems before they become a problem, and detect security vulnerabilities.
2. Test-Driven Design
Test-driven design (TDD) is an approach to software development in which you first write a test that defines what your application should do, then develop a solution for it, and finally make sure that the code fulfills all of its requirements. One big advantage of TDD over more traditional programming methods is that you’re forced to think about how users might interact with your app before you start writing any code, which makes your application easier to use.
3. Static Analysis
Static analysis (also called formal verification) is a program analysis technique that mathematically proves that certain properties are preserved. Static analysis can be applied to many different types of software including operating systems, compilers, hardware, and embedded systems. The purpose of static analysis is to find bugs before they are deployed into production and it is widely used in safety-critical applications such as medical devices, avionics, nuclear power plants, and traffic control systems.
4. Test Coverage
Code coverage is a metric that quantifies how much of your codebase has been tested. Code coverage can be used to compare test cases within a single project or across different projects. Code coverage provides insights into which areas of your code are not being tested, and helps you identify where new tests should be created.
5. Automated Testing
Automated Testing allows developers to make sure that the code they are writing will work, and will continue to work, as they make changes. The automated tests that developers write can be run over and over again by a computer to see if they pass or fail. If a test fails, it helps developers identify what needs fixing. Automated testing is essential for continuous integration and deployment. Developers should always have automated tests in place before making any changes to software so that when something goes wrong it’s easier to track down the problem!
6. Documentation
Software development can be a complicated process, and often involves multiple team members from many different disciplines. This means that there are many opportunities for mistakes to happen along the way, which in turn can cause delays in project deadlines.
7. Reuse Components
Reusing components can make sense for several reasons. You may have one or more existing components that you’re no longer using, but could still be useful to someone else. Or, you may have developed a component that you might want to share with other developers. This can be done by publishing your code as open source on GitHub or similar sites and linking to it from your website. This way people can download and customize your code as they see fit.
This is the reason why any business needs full cycle software development. We offer top-class services in application and software development, visit us at Technogiq IT Solutions for more information.